Data Center Environmental Monitoring Best Practices
Data center managers need to leverage the right tools if they want to successfully monitor mission critical IT devices. However, in an effort to reduce costs, far too often data center managers are tempted into taking unnecessary risks that not only threaten business continuity but put the entire infrastructure at risk.
Fortunately, through best practice approaches, these risks can be mitigated and the optimal levels of environmental monitoring can be achieved.
Best Practice Approach to Data Center Environmental Monitoring
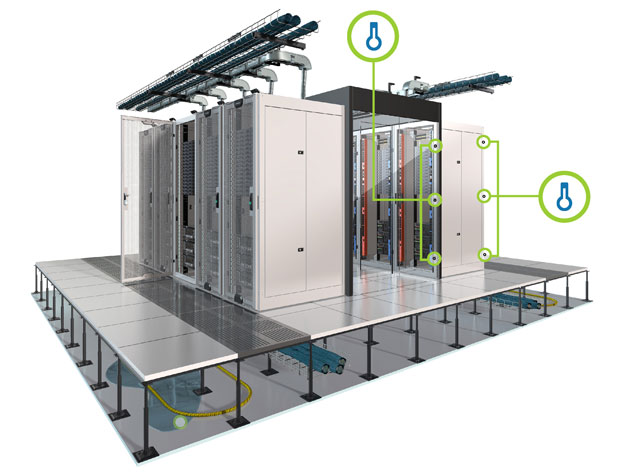
It is important to note that the ASHRAE recommends no less than six temperature sensors per rack. However, the use of six sensors per rack can be a costly expense, which is why many data center managers make the all too common mistake of using fewer sensors and simply monitoring the conditions of the room.
Since room temperatures can vary and subsequently place certain racks at a higher risk, it is important that this common mistake is mitigated by instead using six sensors per rack.
In this vein, the sensors should be placed using one sensor at the top, middle, and bottom of the front of the rack. The same layout should be used at the back of the rack. Through these sensors, data center managers will be able to more accurately determine if there is a heating issue at the rack level.
When room monitoring is used, heating issues are only detected when the room's air conditioning units can no longer compensate for the problem. At this point, it might be too late to resolve the issue without suffering from downtime or rack damage.
While the above layout, which uses six sensors per rack, is the ideal solution, recent studies suggest that data center managers could instead use three measurement points per rack. In this approach, the three sensors would be placed at the bottom front of the rack, the top front of the rack, and the top back of the rack.
Generally speaking, the top back of the rack is often the hottest point of the rack, as such it needs to be carefully monitored. The sensor at the top front of the rack should be used to ensure that cold air is reaching the top of the rack. Finally, the bottom front sensor should be used in conjunction with airflow monitoring to ensure that cold air is reaching the rack.
With the above layout in mind, it is important to note that intake and outtake temperatures need to remain at their optimal levels. Intake temperatures should be 18°-27°C / 64°-80°F, while outtake temperatures should be less than 20°C / 35°F when compared to their respective intake temperature.
Accurate intake and outtake temperature monitoring is vital to maintaining uptime and increasing the lifetime expectancy for data center equipment. While high end systems have auto shutdown capabilities, other models don't have these safeguards.
As such, when racks become overheated, equipment life expectancy is greatly reduced, system availability is at a higher risk, and business continuity is more likely to be impacted. The good news is that by leveraging a best practice approach coupled with the right tools, data center managers can more effectively monitor their vital IT infrastructure.
The Bottom Line: Leverage the Right Tools for Environmental Monitoring
Through the right tools, cost effective environmental monitoring solutions that deliver optimal insights can be leveraged to reduce overheating risks. Raritan's SmartSensor is a strategically engineered environmental monitoring platform that provides accurate data results, heightened levels of insight into operational levels, and real time environmental alerts.
Through these benefits, SmartSensor easily recognizes hot spots, prevents downtime, cools equipment to the optimal levels, and reduces the risks associated with business continuity interruptions.
To learn more about best practice approaches that leverage award winning environmental monitoring technology, contact a member of the Raritan team today at 1-800-724-8090.

