www.magazine-industry-usa.com
17
'23
Written on Modified on
THE STATE OF AUTONOMOUS CONSTRUCTION ADOPTION
Hexagon offers valuable insights into how automation can help firms accomplish their most critical business objectives.

Current penetration and adoption of autonomous solutions in construction
Through a survey of over 1,000 technology leaders from general contractor (GC) construction firms across North America, the United Kingdom and Australia, Hexagon discovered that autonomous technology has undoubtedly hit the gas pedal in the race to adoption. It has crossed the finish line into widespread use, leaving any doubts in the dust. In fact, 84% of firms today incorporate autonomy in their tasks, processes, equipment or systems.
To understand where the industry is in its adoption of autonomy, we condensed and reclassified these firms into three categories: progressive, moderate and laggard.
- Most construction firms (63%) are moderates, meaning they have begun to adopt autonomy in specific areas of their business but are still mainly using autonomous technologies to supplement human activity.
- Coming in at 20.5% are progressive firms, which use four or more autonomous or automated systems within their operations and are more likely to use technologies with full autonomy.
- Only 16.5% of construction firms have yet to adopt autonomy, indicating that laggards risk getting left behind by their competition.
Autonomous technology levels in construction
Among the autonomous technologies used by construction firms, almost 47% are partially or conditionally autonomous. One example of this level of autonomy is a progress-monitoring platform like Avvir, which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse images, track progress and compare building information modelling (BIM) with laser scans of existing conditions to detect discrepancies between design intent and actual construction. The platform requires initial input on what to search for and what is considered “correct” based on the model, after which it can automate the analysis of images to identify deviations. While the software automates the time-consuming aspects of the task, human intervention is still necessary to confirm the findings and take appropriate action.
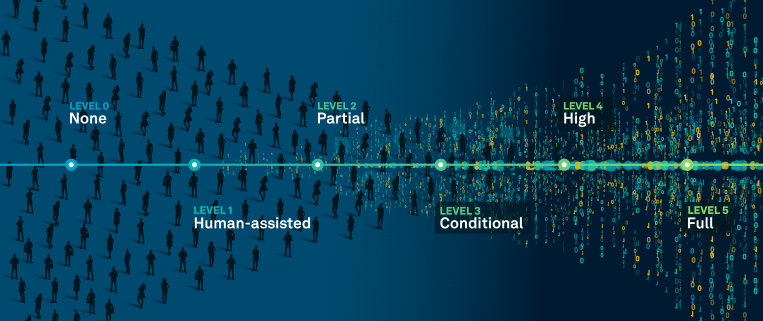
Of the autonomous technologies surveyed firms use, 23% and 30% are split between limited and full autonomy, respectively. Autonomous technology types vary from workflow automation to fully autonomous robotics that can safely navigate remote or hazardous locations without endangering human operators.
Where are construction firms implementing automation in their operations?
Project management workflows represent the most automated area in construction firms, while the adoption of fully autonomous robotics remains relatively low.
About 31% of firms indicated that they use automation in project management workflows. This category includes billing, change management, daily report data, delivery schedules, logistics management, materials requisition and allocation, resource management, scheduling, subcontractor management, time tracking, tool tracking/maintenance/calibration and work packaging.
Other areas in which firms have adopted autonomous technology include workplace safety (28%), quality checks (26%), surveying (26%) and verification (25%).
In contrast, only 16.5% of respondents reported utilising fully autonomous robotics — such as reality capture robots like the BLK ARC and BLK2Fly — in their operations.
The future of autonomous construction
As the construction industry embraces autonomous technologies, we can expect further advancements in sustainability, cross-functional collaboration and safety compliance — among many other benefits. With increasing adoption rates, firms can complete projects faster and with fewer errors, enhancing the industry’s overall performance.
The landscape of autonomous construction is rapidly changing, and maintaining competitiveness necessitates embracing and investing in innovative technologies. By understanding the technology adoption curve and its implications, firms can better position themselves for success in the increasingly automated world of construction.
Learn more about the state of autonomous construction and its benefits in Hexagon’s Autonomous Construction Tech Outlook, “Achieving better project outcomes through autonomy.”
Among the autonomous technologies used by construction firms, almost 47% are partially or conditionally autonomous. One example of this level of autonomy is a progress-monitoring platform like Avvir, which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse images, track progress and compare building information modelling (BIM) with laser scans of existing conditions to detect discrepancies between design intent and actual construction. The platform requires initial input on what to search for and what is considered “correct” based on the model, after which it can automate the analysis of images to identify deviations. While the software automates the time-consuming aspects of the task, human intervention is still necessary to confirm the findings and take appropriate action.

Of the autonomous technologies surveyed firms use, 23% and 30% are split between limited and full autonomy, respectively. Autonomous technology types vary from workflow automation to fully autonomous robotics that can safely navigate remote or hazardous locations without endangering human operators.
Where are construction firms implementing automation in their operations?
Project management workflows represent the most automated area in construction firms, while the adoption of fully autonomous robotics remains relatively low.
About 31% of firms indicated that they use automation in project management workflows. This category includes billing, change management, daily report data, delivery schedules, logistics management, materials requisition and allocation, resource management, scheduling, subcontractor management, time tracking, tool tracking/maintenance/calibration and work packaging.
Other areas in which firms have adopted autonomous technology include workplace safety (28%), quality checks (26%), surveying (26%) and verification (25%).
In contrast, only 16.5% of respondents reported utilising fully autonomous robotics — such as reality capture robots like the BLK ARC and BLK2Fly — in their operations.
The future of autonomous construction
As the construction industry embraces autonomous technologies, we can expect further advancements in sustainability, cross-functional collaboration and safety compliance — among many other benefits. With increasing adoption rates, firms can complete projects faster and with fewer errors, enhancing the industry’s overall performance.
The landscape of autonomous construction is rapidly changing, and maintaining competitiveness necessitates embracing and investing in innovative technologies. By understanding the technology adoption curve and its implications, firms can better position themselves for success in the increasingly automated world of construction.
Learn more about the state of autonomous construction and its benefits in Hexagon’s Autonomous Construction Tech Outlook, “Achieving better project outcomes through autonomy.”

