www.magazine-industry-usa.com
01
'25
Written on Modified on
Benefits of Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) in Terms of ROI
K.A. Gerardino explains how MES contributes to improved financial performance and long-term value creation for manufacturers.

In the highly competitive landscape of modern manufacturing, optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs are key drivers for profitability. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) have emerged as a crucial technology for manufacturers aiming to enhance productivity, improve quality, and maximize return on investment (ROI). This report explores how MES contributes to improved financial performance and long-term value creation for manufacturers.
Global Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Market size is anticipated to be worth US$15.9 billion in 2024, projected to reach US$32.4 billion by 2033 at a 7.2% CAGR from 2024 to 2033, according to Business Research Insights.
The United States Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Market growth is the market leader for North America. Among the industries, the main market drivers are automotive, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods sectors where, on an extreme scale, a great effort goes into optimizing operations, removing as much downtime as possible, and raising the capacity of the productions. Penetration of Industry 4.0 technologies and smart manufacturing in the United States MES market is pushing it ahead. A focus on real-time data and increased visibility in the manufacturing process is keeping the market in line with expectations.
The European Manufacturing Execution System (MES) market share is also expected to expand its market share, driven by manufacturing giants and manufacturing centers within the borders of countries like Germany, the UK, and France. Europe continues to digitize various sectors including the automotive and electronics industry. Europe, mainly focused on its manufacturing units which operate according to stricter regulatory rules, adopts the use of MES as it leads to an efficient traceability performance within European plants.
Asia holds a major portion of the MES market share due to rapid industrialization in countries like China, Japan, and India. Process optimization, quality control, and inventory management needs are fueling the growth of MES solutions across the region. As the region is one of the top producers of electronic devices, automotive components, and consumer goods, manufacturers are becoming increasingly reliant on MES to cope with the demand and ensure efficient production in highly competitive markets.
Understanding MES and Its Role in Manufacturing
MES is a digital system that connects, monitors, and controls complex manufacturing processes in real time. By integrating with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and shop floor automation, MES ensures seamless production workflows, data accuracy, and operational visibility. The system provides insights into resource utilization, production bottlenecks, and quality control, making it indispensable for modern manufacturers.
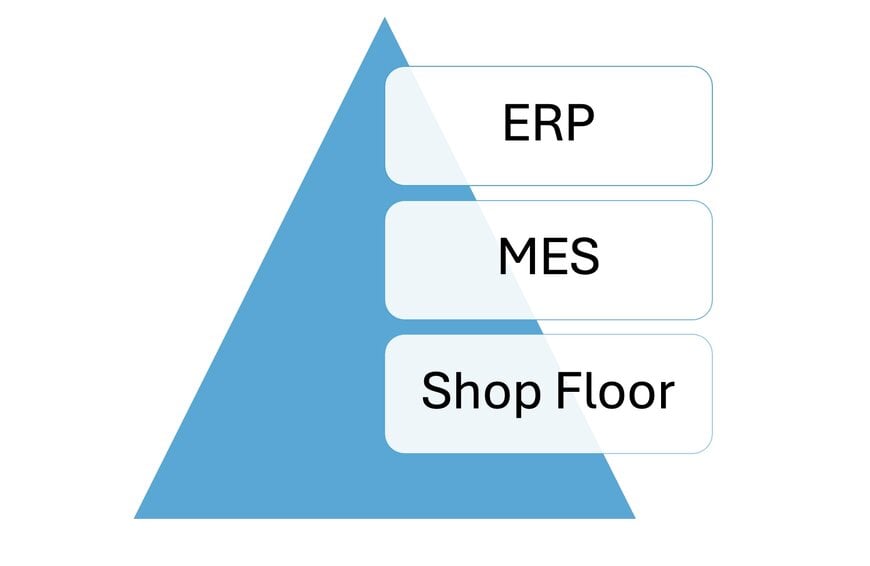
A MES software system captures real-time data from various sources on the factory floor and uses that information to monitor and control manufacturing operations. Here is a general overview of the process:
- Data collection: The system collects data from multiple sources, including machines, sensors, operators and other information systems such as ERP systems or product lifecycle management (PLM) systems. This data can include production rates, machine statuses, inventory levels, quality measurements and more.
- Data integration: The collected data is processed and integrated within the MES system, creating a comprehensive view of the manufacturing environment. This integration helps ensure that the MES has accurate and up-to-date information to work with.
- Production scheduling: Based on the production orders received from higher-level planning systems, the MES generates a production schedule. This schedule considers factors like order priorities, available resources, machine capacities and labor availability.
- Work order management: The system assigns work orders to operators or workstations based on the schedule. It provides operators with instructions, specifications and necessary documentation to help them carry out their tasks. The system tracks the progress of each work order and updates the work-in-progress status in real time.
- Machine and equipment integration: The system interfaces with machines and equipment on the shop floor to monitor their status, collect production data and exchange information. This integration can be achieved through various means such as machine sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) interfaces or communication protocols like OLE (object linking and embedding) for process control (OPC).
- Quality management: Quality data is captured during production, such as measurements, inspections and test results. It enforces quality control procedures, triggers alerts or notifications for quality issues and records quality-related information for analysis and traceability.
- Material and inventory management: The MES tracks the movement of materials and components throughout the production process. It monitors inventory levels, initiates material requisitions or replenishments and helps ensure that the correct materials are available at the right time and in the right quantities.
- Data analysis and reporting: The collected data is analyzed to provide real-time insights and performance metrics. It generates reports, dashboards and visualizations that help management and operators make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement.
- Integration with higher-level systems: The system interfaces with other systems such as ERP, PLM or supply chain management (SCM) systems. This integration allows for the exchange of data, synchronization of information and alignment of manufacturing processes with overall business operations.
Key Benefits of MES in Terms of ROI
1. Increased Operational Efficiency: MES streamlines manufacturing operations by reducing downtime, optimizing machine usage, and minimizing waste. Real-time tracking of production activities allows for quick response to issues, preventing costly disruptions. Manufacturers report an average efficiency increase of 10-20% after implementing MES, leading to higher throughput and revenue growth.
2. Enhanced Product Quality and Reduced Scrap Rates: By providing precise monitoring and control of production processes, MES significantly reduces defects and rework. Automated quality checks and data-driven analytics help maintain compliance with industry standards, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and reduced warranty costs. Studies show that MES adoption can lower defect rates by up to 40%.
3. Improved Inventory Management: MES integrates with supply chain systems to ensure real-time inventory tracking and demand forecasting. This reduces excess stock, minimizes raw material wastage, and improves cash flow management. Manufacturers using MES experience up to 30% reductions in inventory carrying costs.
4. Faster Time-to-Market: MES accelerates production cycles by enabling dynamic scheduling and real-time process adjustments. This agility allows manufacturers to meet market demands quickly and gain a competitive edge. Faster product launches translate to increased sales and market share.
5. Reduced Compliance and Regulatory Risks: Manufacturers in highly regulated industries, such as pharmaceuticals and automotive, benefit from MES’s traceability and audit capabilities. The system ensures compliance with industry standards, reducing the risk of legal penalties and recalls. Companies leveraging MES have reported up to 50% reduction in compliance costs.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making: MES provides actionable insights through advanced analytics and reporting tools. Manufacturers can identify production trends, predict maintenance needs, and optimize workforce allocation. Improved decision-making leads to cost savings and higher profitability.
Challenges for implementing MES systems
Implementing and operating an MES system can come with certain risks and challenges. Here are some common ones:
1. Complex implementation
MES system procurement and implementation can be complex and time-consuming. It requires significant planning, configuration, integration with existing systems and customization to align with specific manufacturing processes.
The complexity of implementation can lead to delays, budget overruns and potential disruptions during the transition phase. The Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Association (MESA) is a global not-for-profit community dedicated to helping member companies successfully implement and apply MES systems and related methodologies.
2. Data integration
Integrating an MES system with other systems such as ERP, PLM or SCM can be challenging. Helping to ensure seamless data exchange and synchronization between different systems might require extensive customization, data mapping and integration efforts. Data inconsistencies or errors during integration can lead to inaccurate information and hinder effective decision-making.
3. Change management
Implementing a paperless MES system often involves changes in business processes, workflows and roles within the organization. Resistance to change from employees or stakeholders can pose challenges and affect user adoption. Proper change management strategies, including training and communication, are crucial to overcome resistance and help ensure a smooth transition and acceptance of the MES system.
4. Data security
MES systems handle large volumes of sensitive production data, including intellectual property, process parameters and quality information. Helping to ensure data security and protecting against unauthorized access or cyberthreats is paramount. Robust security measures, such as data encryption, user access controls and network safeguards, must be in place to mitigate risks.
It’s important to keep these challenges in mind when planning to implement an MES system. But remember that all transformations come with such challenges, and the absence of an MES system can lead to inefficiencies, productivity decreases and reduced competitiveness. With the right approach, these challenges can be overcome.
Case Studies: ROI Achievements with MES Implementation
Several global manufacturers have demonstrated the financial impact of MES adoption:
Automotive Industry
A Tier 1 supplier reported a 15% increase in production efficiency and a 25% reduction in defect rates within the first year of MES implementation. In automotive manufacturing, MES plays a crucial role in coordinating complex assembly lines. They track the progress of vehicles on the assembly line, monitor the availability of components and synchronize operations across different workstations.
MES in the automotive industry often focuses on helping to ensure quality control, managing recalls and maintaining compliance with industry standards.
Electronics Manufacturing
A leading electronics manufacturer achieved a 20% decrease in scrap rates and a 12% improvement in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). MES systems in the electronics industry focus on managing the intricate processes involved in manufacturing electronic components and devices.
They handle bill of materials (BOM) management, help ensure accurate component tracking, monitor equipment performance and provide real-time visibility into production processes. MES systems in this industry often integrate with equipment such as pick-and-place machines and automated testing systems.
Food & Beverage Sector
A major food processing company realized a 30% reduction in inventory costs and a 10% increase in on-time deliveries after deploying MES. In the food and beverage industry, MES systems help manage the complexities of recipe management, formulation and compliance with food safety regulations.
They track ingredients, manage recipes, monitor production rates and enforce quality control procedures. MES in this industry might also include features for managing lot traceability, allergen control and compliance with industry-specific standards.
Aerospace and defense
In aerospace and defense manufacturing, MES systems help ensure compliance with stringent regulations, manage complex assembly processes and maintain high levels of quality control.
They track the movement of parts, manage work orders for aircraft or defense system assembly, monitor compliance with industry standards and facilitate the documentation of testing and inspection processes.
Consumer goods
MES systems in the consumer goods industry assist in managing the production of fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) such as packaged foods, beverages, personal care products and household items.
They focus on optimizing production efficiency, managing packaging variations and coordinating multiple production lines. MES systems in this industry often integrate with packaging equipment and provide real-time data on production rates, quality parameters and inventory levels.
Trends in MES systems
Several digital transformation trends are shaping the evolution of MES systems in recent years.
1. Cloud-based MES: Cloud computing has gained traction in the manufacturing industry, and MES software is increasingly being offered as a cloud-based solution. Cloud-based MES systems provide benefits such as scalability, flexibility, reduced infrastructure costs and easier access to data from multiple locations. They also facilitate integration with other cloud-based applications and enable real-time collaboration.
2. IIoT integration: The integration of MES systems with the industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a significant trend. MES systems use IIoT technologies to collect data from sensors, machines and connected devices in real-time. This integration allows for enhanced visibility, predictive analytics, remote monitoring and optimization of manufacturing processes.
3. Big data analytics: MES systems are using big data analytics capabilities to process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated in manufacturing operations. Advanced analytics algorithms and machine learning techniques are applied to identify patterns, correlations and actionable insights. This helps optimize production, improve quality and enable predictive maintenance.
4. Mobile applications: Mobile applications are increasingly being integrated into MES systems to enable real-time access to data and functions from smartphones and tablets. Operators, supervisors and managers can monitor and control manufacturing processes, view production dashboards and receive notifications on their mobile devices. Mobile MES apps improve operational agility and enable on-the-go decision-making.
5. Integration with supply chain systems: MES systems are expanding their integration capabilities to connect with supply chain systems. This integration allows for seamless information flow between MES, ERP and SCM systems, enabling improved supply chain visibility, demand planning and synchronization. It facilitates better collaboration with suppliers, customers and logistics partners.
6. AI and machine learning: AI and machine learning technologies are being applied in MES systems to automate decision-making, optimize processes and enable predictive capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze historical data, identify anomalies, predict production outcomes and recommend process improvements. This trend empowers MES systems to provide real-time intelligent insights and support data-driven decision-making.
7. Enhanced user interfaces and visualization: MES systems are focusing on providing intuitive user interfaces and advanced visualization capabilities. Interactive dashboards, 3D visualization, augmented reality and virtual reality are being incorporated to enhance the user experience and facilitate a better understanding of production data. This enables operators and managers to quickly identify trends, anomalies and areas for improvement.
8. Compliance and regulatory features: With increasingly stringent regulations in various industries, MES systems are incorporating more robust compliance and regulatory features. This includes features for electronic record keeping, audit trails, documentation management and adherence to industry-specific standards and regulations. MES systems play a critical role in ensuring compliance with regulations such as FDA requirements in pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing.
These trends reflect the industry's focus on using advanced technologies, connectivity and data analytics to improve efficiency, agility and decision-making in manufacturing operations. Implementing these trends in MES systems can provide manufacturers with a competitive edge.
Top Manufacturing Execution System Companies
Here is the top MES companies based on Business Research Insights report:
Rockwell Automation, Inc. (United States) is a global leader in industrial automation and digital transformation. Its FactoryTalk® ProductionCentre MES provides real-time monitoring and control, with a strong presence in the automotive, life sciences, and food & beverage industries. The company is particularly known for seamless integration with Allen-Bradley PLCs and its wide range of automation software. Similarly, Emerson Electric Co. (United States) offers Syncade MES, a system widely adopted in pharmaceutical and life sciences sectors. With deep expertise in process automation and control, Emerson excels in supporting regulatory compliance and batch process manufacturing.

FactoryTalk Analytics Image: Rockwell Automation
Siemens AG (Germany) is another major player, with its Opcenter MES tightly integrated into Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM). Siemens combines advanced digital twin technology with AI-driven analytics, making it dominant in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and semiconductors. Its adaptability to Industry 4.0 makes it a preferred choice for smart manufacturing. Meanwhile, Schneider Electric S.E. (France) provides the EcoStruxure™ Manufacturing Operation, offering sustainability-focused MES solutions. Leveraging its strengths in energy management and industrial automation, Schneider’s MES integrates effectively with SCADA, PLCs, and ERP systems, supporting industries such as oil & gas, mining, and food processing.
Dassault Systèmes SA (France) delivers DELMIA Apriso MES, enabling global manufacturing visibility and supporting both discrete and process manufacturing. Leveraging its strong capabilities in 3D design, simulation, and digital twin technologies, Dassault’s MES is widely used in aerospace, industrial equipment, and transportation sectors. On the other hand, SAP SE (Germany) provides the Digital Manufacturing Cloud (DMC), which integrates MES with ERP systems and AI-driven analytics. With deep integration into SAP S/4HANA and strong capabilities in end-to-end supply chain digitalization, SAP serves large-scale enterprises across automotive, electronics, and pharmaceutical industries.

DELMIA Apriso - MOM Solutions Image: Dassault Systèmes
1. Increased Operational Efficiency: MES streamlines manufacturing operations by reducing downtime, optimizing machine usage, and minimizing waste. Real-time tracking of production activities allows for quick response to issues, preventing costly disruptions. Manufacturers report an average efficiency increase of 10-20% after implementing MES, leading to higher throughput and revenue growth.
2. Enhanced Product Quality and Reduced Scrap Rates: By providing precise monitoring and control of production processes, MES significantly reduces defects and rework. Automated quality checks and data-driven analytics help maintain compliance with industry standards, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and reduced warranty costs. Studies show that MES adoption can lower defect rates by up to 40%.
3. Improved Inventory Management: MES integrates with supply chain systems to ensure real-time inventory tracking and demand forecasting. This reduces excess stock, minimizes raw material wastage, and improves cash flow management. Manufacturers using MES experience up to 30% reductions in inventory carrying costs.
4. Faster Time-to-Market: MES accelerates production cycles by enabling dynamic scheduling and real-time process adjustments. This agility allows manufacturers to meet market demands quickly and gain a competitive edge. Faster product launches translate to increased sales and market share.
5. Reduced Compliance and Regulatory Risks: Manufacturers in highly regulated industries, such as pharmaceuticals and automotive, benefit from MES’s traceability and audit capabilities. The system ensures compliance with industry standards, reducing the risk of legal penalties and recalls. Companies leveraging MES have reported up to 50% reduction in compliance costs.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making: MES provides actionable insights through advanced analytics and reporting tools. Manufacturers can identify production trends, predict maintenance needs, and optimize workforce allocation. Improved decision-making leads to cost savings and higher profitability.
Challenges for implementing MES systems
Implementing and operating an MES system can come with certain risks and challenges. Here are some common ones:
1. Complex implementation
MES system procurement and implementation can be complex and time-consuming. It requires significant planning, configuration, integration with existing systems and customization to align with specific manufacturing processes.
The complexity of implementation can lead to delays, budget overruns and potential disruptions during the transition phase. The Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Association (MESA) is a global not-for-profit community dedicated to helping member companies successfully implement and apply MES systems and related methodologies.
2. Data integration
Integrating an MES system with other systems such as ERP, PLM or SCM can be challenging. Helping to ensure seamless data exchange and synchronization between different systems might require extensive customization, data mapping and integration efforts. Data inconsistencies or errors during integration can lead to inaccurate information and hinder effective decision-making.
3. Change management
Implementing a paperless MES system often involves changes in business processes, workflows and roles within the organization. Resistance to change from employees or stakeholders can pose challenges and affect user adoption. Proper change management strategies, including training and communication, are crucial to overcome resistance and help ensure a smooth transition and acceptance of the MES system.
4. Data security
MES systems handle large volumes of sensitive production data, including intellectual property, process parameters and quality information. Helping to ensure data security and protecting against unauthorized access or cyberthreats is paramount. Robust security measures, such as data encryption, user access controls and network safeguards, must be in place to mitigate risks.
It’s important to keep these challenges in mind when planning to implement an MES system. But remember that all transformations come with such challenges, and the absence of an MES system can lead to inefficiencies, productivity decreases and reduced competitiveness. With the right approach, these challenges can be overcome.
Case Studies: ROI Achievements with MES Implementation

Several global manufacturers have demonstrated the financial impact of MES adoption:
Automotive Industry
A Tier 1 supplier reported a 15% increase in production efficiency and a 25% reduction in defect rates within the first year of MES implementation. In automotive manufacturing, MES plays a crucial role in coordinating complex assembly lines. They track the progress of vehicles on the assembly line, monitor the availability of components and synchronize operations across different workstations.
MES in the automotive industry often focuses on helping to ensure quality control, managing recalls and maintaining compliance with industry standards.
Electronics Manufacturing
A leading electronics manufacturer achieved a 20% decrease in scrap rates and a 12% improvement in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). MES systems in the electronics industry focus on managing the intricate processes involved in manufacturing electronic components and devices.
They handle bill of materials (BOM) management, help ensure accurate component tracking, monitor equipment performance and provide real-time visibility into production processes. MES systems in this industry often integrate with equipment such as pick-and-place machines and automated testing systems.
Food & Beverage Sector
A major food processing company realized a 30% reduction in inventory costs and a 10% increase in on-time deliveries after deploying MES. In the food and beverage industry, MES systems help manage the complexities of recipe management, formulation and compliance with food safety regulations.
They track ingredients, manage recipes, monitor production rates and enforce quality control procedures. MES in this industry might also include features for managing lot traceability, allergen control and compliance with industry-specific standards.
Aerospace and defense
In aerospace and defense manufacturing, MES systems help ensure compliance with stringent regulations, manage complex assembly processes and maintain high levels of quality control.
They track the movement of parts, manage work orders for aircraft or defense system assembly, monitor compliance with industry standards and facilitate the documentation of testing and inspection processes.
Consumer goods
MES systems in the consumer goods industry assist in managing the production of fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) such as packaged foods, beverages, personal care products and household items.
They focus on optimizing production efficiency, managing packaging variations and coordinating multiple production lines. MES systems in this industry often integrate with packaging equipment and provide real-time data on production rates, quality parameters and inventory levels.
Trends in MES systems
Several digital transformation trends are shaping the evolution of MES systems in recent years.
1. Cloud-based MES: Cloud computing has gained traction in the manufacturing industry, and MES software is increasingly being offered as a cloud-based solution. Cloud-based MES systems provide benefits such as scalability, flexibility, reduced infrastructure costs and easier access to data from multiple locations. They also facilitate integration with other cloud-based applications and enable real-time collaboration.
2. IIoT integration: The integration of MES systems with the industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a significant trend. MES systems use IIoT technologies to collect data from sensors, machines and connected devices in real-time. This integration allows for enhanced visibility, predictive analytics, remote monitoring and optimization of manufacturing processes.
3. Big data analytics: MES systems are using big data analytics capabilities to process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated in manufacturing operations. Advanced analytics algorithms and machine learning techniques are applied to identify patterns, correlations and actionable insights. This helps optimize production, improve quality and enable predictive maintenance.
4. Mobile applications: Mobile applications are increasingly being integrated into MES systems to enable real-time access to data and functions from smartphones and tablets. Operators, supervisors and managers can monitor and control manufacturing processes, view production dashboards and receive notifications on their mobile devices. Mobile MES apps improve operational agility and enable on-the-go decision-making.
5. Integration with supply chain systems: MES systems are expanding their integration capabilities to connect with supply chain systems. This integration allows for seamless information flow between MES, ERP and SCM systems, enabling improved supply chain visibility, demand planning and synchronization. It facilitates better collaboration with suppliers, customers and logistics partners.
6. AI and machine learning: AI and machine learning technologies are being applied in MES systems to automate decision-making, optimize processes and enable predictive capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze historical data, identify anomalies, predict production outcomes and recommend process improvements. This trend empowers MES systems to provide real-time intelligent insights and support data-driven decision-making.
7. Enhanced user interfaces and visualization: MES systems are focusing on providing intuitive user interfaces and advanced visualization capabilities. Interactive dashboards, 3D visualization, augmented reality and virtual reality are being incorporated to enhance the user experience and facilitate a better understanding of production data. This enables operators and managers to quickly identify trends, anomalies and areas for improvement.
8. Compliance and regulatory features: With increasingly stringent regulations in various industries, MES systems are incorporating more robust compliance and regulatory features. This includes features for electronic record keeping, audit trails, documentation management and adherence to industry-specific standards and regulations. MES systems play a critical role in ensuring compliance with regulations such as FDA requirements in pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing.
These trends reflect the industry's focus on using advanced technologies, connectivity and data analytics to improve efficiency, agility and decision-making in manufacturing operations. Implementing these trends in MES systems can provide manufacturers with a competitive edge.
Top Manufacturing Execution System Companies
Here is the top MES companies based on Business Research Insights report:
Rockwell Automation, Inc. (United States) is a global leader in industrial automation and digital transformation. Its FactoryTalk® ProductionCentre MES provides real-time monitoring and control, with a strong presence in the automotive, life sciences, and food & beverage industries. The company is particularly known for seamless integration with Allen-Bradley PLCs and its wide range of automation software. Similarly, Emerson Electric Co. (United States) offers Syncade MES, a system widely adopted in pharmaceutical and life sciences sectors. With deep expertise in process automation and control, Emerson excels in supporting regulatory compliance and batch process manufacturing.

FactoryTalk Analytics Image: Rockwell Automation
Siemens AG (Germany) is another major player, with its Opcenter MES tightly integrated into Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM). Siemens combines advanced digital twin technology with AI-driven analytics, making it dominant in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and semiconductors. Its adaptability to Industry 4.0 makes it a preferred choice for smart manufacturing. Meanwhile, Schneider Electric S.E. (France) provides the EcoStruxure™ Manufacturing Operation, offering sustainability-focused MES solutions. Leveraging its strengths in energy management and industrial automation, Schneider’s MES integrates effectively with SCADA, PLCs, and ERP systems, supporting industries such as oil & gas, mining, and food processing.
Dassault Systèmes SA (France) delivers DELMIA Apriso MES, enabling global manufacturing visibility and supporting both discrete and process manufacturing. Leveraging its strong capabilities in 3D design, simulation, and digital twin technologies, Dassault’s MES is widely used in aerospace, industrial equipment, and transportation sectors. On the other hand, SAP SE (Germany) provides the Digital Manufacturing Cloud (DMC), which integrates MES with ERP systems and AI-driven analytics. With deep integration into SAP S/4HANA and strong capabilities in end-to-end supply chain digitalization, SAP serves large-scale enterprises across automotive, electronics, and pharmaceutical industries.

DELMIA Apriso - MOM Solutions Image: Dassault Systèmes
In the United States, the General Electric Company offers GE Digital’s Proficy MES, a solution focused on real-time production management, predictive analytics, and AI-powered industrial operations. Its applications are especially strong in energy, aviation, and heavy machinery, and the system supports edge computing and IIoT-based operations. Likewise, ABB Ltd. (Switzerland) provides ABB Ability™ Manufacturing Operations Management, with robust adoption in metals, chemicals, and discrete manufacturing. ABB’s MES integrates seamlessly with robotic process automation (RPA) and AI, reflecting its leadership in robotics and industrial automation.
Atos SE (France) focuses on cloud-based MES solutions with strong integration of cybersecurity, big data, and AI. Its partnerships with Siemens and SAP further strengthen its position in smart manufacturing, particularly in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. Finally, Honeywell International Inc. (United States) offers Honeywell Forge MES, a platform designed for enterprise-wide manufacturing optimization. With strong applications in chemicals, oil & gas, and industrial automation, Honeywell integrates MES with AI, IIoT, and real-time monitoring to support predictive maintenance, supply chain visibility, and plant-wide connectivity.
Final Thoughts
Siemens, Rockwell, and Schneider Electric continue to set the pace in automotive and industrial automation, building on their strengths in smart manufacturing and advanced automation systems. SAP and Dassault Systèmes stand out in enterprise integration, particularly with digital twins, simulation, and supply chain digitalization. In the energy, process, and heavy industries, GE, ABB, and Honeywell remain dominant with their expertise in predictive analytics, IIoT integration, and real-time optimization. Atos and Emerson, meanwhile, carve out their niche with highly specialized MES solutions designed for aerospace, life sciences, and other tightly regulated sectors. Together, these companies are shaping the future of MES—each addressing unique industry needs while collectively driving innovation across global manufacturing.
For manufacturers, investing in MES is more than a technology upgrade—it’s a pathway to measurable business gains. From boosting efficiency and reducing waste to ensuring consistent quality, the benefits are clear. The return on investment shows up not just in productivity and cost savings, but also in better compliance, stronger customer satisfaction, and quicker responses to shifting market demands. As Industry 4.0 accelerates, MES will remain a cornerstone of smart manufacturing strategies. Companies that embrace it will be better equipped to compete globally, adapt to change, and achieve sustainable long-term growth in an increasingly digital world.

